Leveraging Technology for Social Impact
Related Services
Credits

At Pastilla, we are committed to creating accessible, secure, and scalable web solutions that drive social impact.
While our core focus remains on user-centered design and development, we are excited about the potential of integrating emerging technologies like AI, blockchain, and IoT into our future projects. These innovations offer exciting opportunities to enhance user experience, increase transparency, and enable data-driven decision-making, which can further amplify the impact of our digital platforms and inspire a brighter future for social good.
Some of our key projects illustrate how web development can create meaningful social impact:
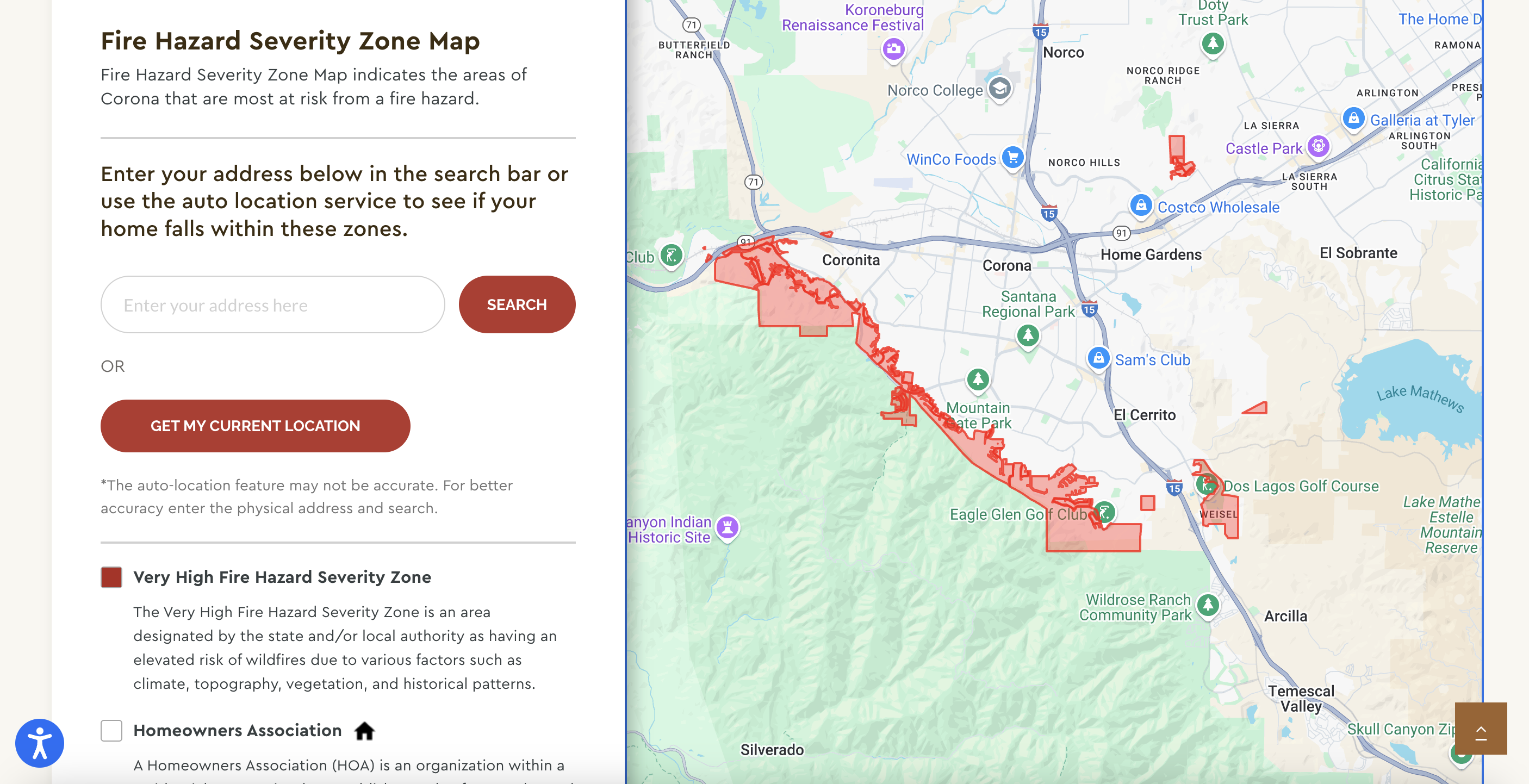
Firesafe Corona: We developed an interactive map for the Firesafe Corona initiative, providing residents with real-time information about fire hazards in their area. This tool helps to enhance community awareness and preparedness.
Watts Rising: The tree dedication app we developed for the Watts community encourages local tree planting by allowing residents to dedicate trees in honor of loved ones. It also fosters community involvement and promotes environmental stewardship in the Watts area.

LA Parks App: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, we created an intuitive app for the City of Los Angeles Department of Recreation and Parks. The app simplifies program discovery and registration, improves communication for staff, and promotes greater community engagement.

myLAB Box: Our collaboration with myLAB Box, an online-based health and wellness medical testing provider, showcases our ability to manage sensitive health data securely. From 2015 until 2023, we supported myLAB Box in updating and maintaining their WordPress website, which included three redesigns, rebranding, hosting migration, and ongoing software, security, SEO, and e-commerce support. An important part of our work was creating a separate data processing platform to handle sensitive medical information securely while ensuring user privacy and building trust in digital health solutions. This project improved access to affordable and convenient medical testing, allowing users to manage their health from the safety of their homes.
These projects highlight the power of web development to drive social good, and emerging technologies like AI could further enhance our initiatives.
In this article, we’ll explore how these new technologies can enhance our social impact even further. We’ll also examine the ethical considerations that guide our approach to integrating them into our work, underscoring the importance of responsible technology use in driving social good.
AI: Enhancing Efficiency and Social Equity
AI’s ability to analyze data and recognize patterns is slowly reshaping how we live and work and transforming our world.
In education, for instance, AI is paving the way for personalized learning experiences. Platforms that leverage AI can adapt educational content to suit individual students’ needs, helping to close the achievement gap across different socioeconomic backgrounds.
Duolingo is an excellent example of AI in education. The platform uses machine learning algorithms to personalize user language learning experiences. It adapts lessons based on individual progress, strengths, and weaknesses, providing tailored exercises that help reinforce learning.
Duolingo’s AI also analyzes user performance to suggest appropriate next steps. This personalization helps ensure that learners receive the support they need, regardless of their initial skill level, contributing to better educational outcomes across diverse backgrounds.
In healthcare, AI is making waves by improving diagnostic processes and treatment plans. Additionally, AI algorithms can analyze medical images, assisting doctors in earlier disease detection.
Take the da Vinci surgical system, for example. It is a revolutionary robotic platform that combines precision, control, and advanced visualization to enhance minimally invasive surgeries. It features robotic arms with surgical instruments that mimic a surgeon’s hand movements, providing superior skill and a high-definition, 3D view of the surgical site. This technology enables precise maneuvers in tight spaces, minimizing tissue trauma and leading to faster patient recovery.
Operated by the surgeon from a console, the system integrates human expertise with robotic capabilities, demonstrating the positive impact of AI and robotics on surgical outcomes and patient care.
Ethical considerations for using AI technology
As we embrace these advancements, we must confront some critical ethical considerations. For instance, AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate bias if trained on data reflecting existing inequalities. A study on three different commercially released facial-analysis programs by major tech companies, conducted by MIT and Stanford, discovered skin type and gender biases. The algorithm used in this technology had higher error rates in identifying the gender of darker-skinned and female faces than lighter-skinned and male faces.
Privacy is another significant concern when using AI. Organizations using it must prioritize robust data protection measures to safeguard user information. AI played a crucial role in the Cambridge Analytica scandal by using advanced algorithms to analyze the large amounts of data collected from Facebook users. The company used machine learning techniques to segment users based on their behaviors, preferences, and psychological profiles. The data they collected allowed them to create targeted political ads tailored to specific audiences, significantly influencing voter behavior. Ultimately, personal data from millions of Facebook users was harvested without consent and used to influence electoral outcomes.
In the education sector, there are concerns that reliance on AI could significantly reduce human interaction and negatively impact critical thinking skills. There are studies highlighting how AI may reduce face-to-face engagement in classrooms, leading to a lack of social development for students. Moreover, the convenience of AI can lead to overreliance, jeopardizing the development of essential problem-solving abilities.
We should all keep in mind that while AI holds incredible promise for enhancing efficiency and fostering social equity, we must address these ethical challenges as we integrate these technologies into our lives. Moreover, as AI takes over tasks traditionally performed by humans, we need to find a balance between efficiency and maintaining meaningful human interactions, especially in sensitive areas like healthcare and education.
IoT: Data-Driven Decision-Making in Smart Cities, Agriculture, and Healthcare
By integrating devices like sensors and smart meters into different aspects of our lives, the Internet of Things (IoT) enables the collection of real-time information that enhances resource optimization, condition monitoring, and informed decision-making.
It is a proven fact that IoT technologies are making urban areas more sustainable. By monitoring air quality, managing traffic flow, and optimizing energy consumption, cities can enhance residents’ quality of life while minimizing their environmental footprint. Real-time data connectivity allows for smarter urban planning and more efficient resource allocation.
For example, Cisco’s Connected Streetlights program transforms traditional street lighting into innovative, energy-efficient solutions. They equip street lights with sensors so cities can monitor energy usage, detect outages, and adjust lighting levels based on real-time conditions. This step reduces energy costs, enhances public safety, and informs urban planning by analyzing pedestrian activity and traffic patterns.
In smart agriculture, IoT devices help to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. The collected data empowers farmers to make informed decisions that can boost yield and reduce waste.
One of such IoT tools is John Deere’s Precision Agriculture solution through its Operations Center, which aggregates data from various equipment and sensors. Thanks to it, farmers can analyze field performance, manage inputs efficiently, and plan for future planting and harvesting activities.
In healthcare, IoT is used for remote monitoring of patients, which can lead to early detection of health issues and fewer hospital admissions. Wearable devices, such as Fitbit fitness trackers and Apple Watch, and sensors like continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) from Dexcom transmit vital data directly to healthcare providers. The collected data enables timely interventions and personalized care, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Ethical Considerations for IoT
There are risks to using technology that’s so involved in our lives, one of the bigger ones is security vulnerabilities; the more devices are connected, the greater are the opportunities for cyberattacks.
Moreover, data breaches pose serious threats as IoT devices often handle personal and sensitive information. In 2021, Fitbit, a popular wearable fitness tracker, faced scrutiny after a data breach exposed sensitive user information. The incident highlighted the potential risks associated with personal health data collected by IoT devices. It emphasized the need for organizations to establish robust encryption and access controls to safeguard user data from unauthorized access.
The widespread use of IoT has raised valid concerns about digital divides. The COVID-19 pandemic worsened existing digital gaps, especially in telehealth. Many rural and underserved communities lacked reliable internet access and digital literacy, making it challenging for residents to use IoT-based healthcare solutions such as remote monitoring devices. As IoT technology becomes more prevalent, those lacking access to necessary infrastructure or digital literacy skills may be further marginalized, exacerbating existing inequalities.
Blockchain: Building Trust and Accountability
New kid on the block, blockchain, gives us an option to use a decentralized, tamper-proof record of transactions, which helps foster greater trust between organizations and their communities, whether we’re talking about tracking charitable donations, verifying product origins, or securing sensitive medical data.
In the area of supply chain integrity, for example, blockchain can offer an immutable record of a product’s journey from its source to the consumer.
Companies like Provenance utilize blockchain to verify that products labeled as fair trade or organic genuinely meet those standards. When a product is labeled as fair trade or organic, Provenance tracks and verifies each step in the supply chain, documenting details such as sourcing practices, processing, and transportation. This information is stored on the blockchain, making it easily accessible and verifiable by consumers. By scanning a QR code or accessing a dedicated webpage, consumers can see the complete history of the product, including certifications and compliance with ethical standards.
Another impactful use of blockchain is in charitable donations, where it can establish transparent records that guarantee funds are used as intended. Organizations such as GiveTrack give donors a real-time view of how their contributions are allocated and spent, increasing trust and encouraging more robust support for charitable initiatives. When a donor contributes to a project, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, providing a tamper-proof ledger of how funds are allocated. Donors can then access a unique tracking interface that shows the journey of their contributions, including details on how the funds are spent and the impact achieved.
Ethical Considerations for Blockchain
One significant concern for blockchain use is the environmental impact of blockchain mining. The process can be energy-intensive, contributing to ecological degradation. Ongoing efforts aim to create more energy-efficient blockchain systems, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) mechanisms, which consume considerably less energy than traditional mining methods.
Another challenge is balancing transparency with privacy. While blockchain’s inherent openness can enhance trust, it raises concerns about protecting sensitive data. Striking a balance between maintaining accountability and safeguarding individual privacy remains essential.
Additionally, verification challenges persist. Although blockchain facilitates transparency, ensuring that the information recorded is accurate and authentic is crucial for its effective functioning. Organizations must focus on developing robust verification methods to maintain the integrity of the data recorded on the blockchain.
For example, Everledger is a blockchain platform that tracks diamonds’ provenance to prevent fraud and conflict sourcing. It relies on accurate data input from various sources, including gemologists and retailers. To ensure the integrity of the data recorded on the blockchain, Everledger has developed partnerships with industry experts to establish robust verification methods, ensuring that only authenticated diamonds get into the system.
Balancing Ethics and the Promise of Emerging Technologies
The rapid advancement of AI, blockchain, and IoT brings exciting possibilities for creating a more equitable and sustainable world. Still, it also raises critical ethical questions that cannot be ignored. At Pastilla, we are committed to leveraging these technologies responsibly, ensuring that our solutions prioritize fairness, transparency, and security.
As these technologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly shape the future of social impact, enabling better educational outcomes, healthcare access, and efficient resource management across various sectors. We can use their full potential for social good, but we must take a step back to consider the implications of using these technologies and act thoughtfully.
